5MG
This product is for research purposes only. Not for human consumption.
Purity: >99% (HPLC verified)
Formulation: Lyophilized powder
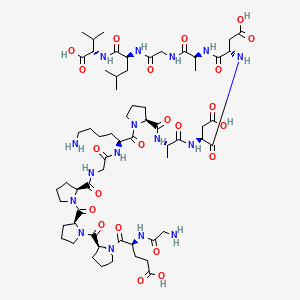
Molecular Formula: C62H98N16O22
Molecular Weight: 1419.5 g/mol
CAS Number: 137525-51-0
PubChem CID: 9941957
BPC-157
Overview
BPC-157, also known as Body Protection Compound-157, is a synthetic pentadecapeptide derived from a protective protein found in human gastric juice. This remarkable 15-amino acid sequence (Gly-Glu-Pro-Pro-Pro-Gly-Lys-Pro-Ala-Asp-Asp-Ala-Gly-Leu-Val) has demonstrated extraordinary healing and protective properties across multiple tissue types and organ systems in extensive preclinical research.
Originally isolated from gastric secretions, BPC-157 is stable in gastric acid and maintains biological activity across various administration routes. The peptide has shown cytoprotective effects throughout the gastrointestinal tract, musculoskeletal system, nervous system, and cardiovascular system.
Its unique mechanism of promoting angiogenesis while simultaneously reducing inflammation has made it a subject of intense research interest for tissue repair and regeneration applications.
Mechanism of Action
BPC-157 exerts its therapeutic effects through multiple interconnected molecular pathways. The peptide promotes angiogenesis by upregulating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and stimulating the formation of new blood vessels, which is critical for delivering nutrients and oxygen to healing tissues.
It modulates the nitric oxide (NO) pathway, maintaining optimal NO levels that support vascular health and tissue perfusion. BPC-157 enhances collagen deposition and organization during wound healing by stimulating fibroblast activity and regulating the expression of growth factors including fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and epidermal growth factor (EGF).
The peptide exhibits potent anti-inflammatory properties by modulating cytokine production, reducing pro-inflammatory mediators like TNF-α and IL-6 while promoting anti-inflammatory responses. It stabilizes cellular membranes, protects against oxidative stress, and supports mitochondrial function.
In the gastrointestinal tract, BPC-157 accelerates epithelial regeneration, protects the gastric mucosa, and promotes healing of ulcers through enhanced mucosal blood flow and growth factor activity. The peptide also influences neurotransmitter systems, particularly dopaminergic and GABAergic pathways, contributing to its neuroprotective effects.
Additionally, BPC-157 has demonstrated the ability to modulate the expression of genes involved in tissue repair, cellular migration, and extracellular matrix remodeling.
Research Findings
The research portfolio for BPC-157 is extensive, spanning over three decades of preclinical investigations. Studies have consistently demonstrated the peptide's ability to accelerate healing of tendon injuries, with research showing enhanced recovery from Achilles tendon transection, improved tendon-to-bone healing, and faster restoration of biomechanical properties in damaged tendons.
Musculoskeletal Research
In muscle injury models, BPC-157 has shown remarkable efficacy in promoting recovery from muscle crush injuries, lacerations, and contusions, with studies documenting reduced inflammation, faster tissue regeneration, and improved functional recovery. Ligament healing research has revealed that BPC-157 promotes the healing of medial collateral ligament injuries and other connective tissue damage through enhanced collagen synthesis and angiogenesis.
Bone healing studies have demonstrated improved fracture healing and osseointegration, though this represents a smaller subset of the research.
Gastrointestinal Protection
In the gastrointestinal system, extensive research has shown BPC-157's protective and healing effects across the entire GI tract - from esophageal lesions to colonic inflammation. Studies document accelerated healing of gastric and duodenal ulcers, protection against NSAID-induced gastropathy, improvement of inflammatory bowel disease in animal models, and healing of intestinal anastomoses and fistulas.
Cardiovascular and Neurological Effects
Cardiovascular research has revealed protective effects against various cardiac injuries, with studies showing benefits in arrhythmia models, protection against potassium-induced cardiac damage, and improved recovery from ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Neurological research indicates neuroprotective properties, with studies demonstrating benefits in traumatic brain injury models, improved recovery from peripheral nerve injuries, and protective effects against neurotoxins. The peptide has also shown promise in liver protection studies, demonstrating hepatoprotective effects against toxic injury and improved healing of liver damage.
Wound Healing Studies
Research into wound healing has consistently shown accelerated closure of various wound types including burns, with improved tissue quality and reduced scar formation. While the majority of research has been conducted in rodent models, the consistency of findings across multiple tissue types, injury models, and research groups provides compelling evidence for BPC-157's regenerative properties.
However, it's important to note that comprehensive human clinical trials remain limited, and most safety and efficacy data comes from animal studies.
Research Applications
- Tendon injury healing and recovery research
- Ligament repair and regeneration studies
- Muscle injury and tissue damage research
- Gastrointestinal ulcer healing and protection studies
- Inflammatory bowel disease research
- Wound healing and burn treatment studies
- Bone fracture healing research
- Cardiovascular protection and repair studies
- Neuroprotection and nerve injury research
- Post-surgical healing enhancement research
- Sports medicine and athletic injury studies
- Chronic inflammation research
- Vascular health and angiogenesis studies
Safety Profile
BPC-157 has demonstrated a remarkably favorable safety profile across numerous preclinical studies, with no significant toxic effects reported even at doses far exceeding therapeutic ranges. Animal studies have shown good tolerability across multiple administration routes including oral, intraperitoneal, intramuscular, and topical applications. The peptide has shown no evidence of genotoxicity, carcinogenicity, or teratogenicity in research models. However, it is crucial to note that comprehensive human safety data remains limited, as most research has been conducted in animal models, primarily rodents. No large-scale Phase III clinical trials have been completed in humans, and long-term safety data in human subjects is lacking. The peptide is not approved by regulatory agencies such as the FDA or EMA for therapeutic use, and is currently available only for research purposes. Potential users should be aware that while preclinical safety appears excellent, the absence of extensive human clinical trials means unknown risks may exist. Reported anecdotal side effects from non-clinical use have been minimal, typically limited to mild injection site reactions. The optimal dosing, frequency, and duration of use in humans have not been established through rigorous clinical trials. As with any research compound, appropriate caution, informed consent, and medical supervision are essential.
Scientific References
Research Use Only
This product is intended for research purposes only and is not for human consumption, therapeutic use, or diagnostic applications. Please ensure compliance with all applicable regulations and institutional guidelines.