2mg
This product is for research purposes only. Not for human consumption.
Purity: >98% (HPLC verified)
Formulation: Lyophilized powder
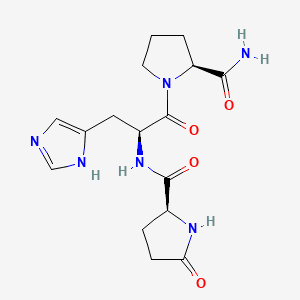
Molecular Formula: C55H75N17O13
Molecular Weight: 1182.3 g/mol
CAS Number: 33515-09-2
PubChem CID: 638678
Gonadorelin
Overview
Gonadorelin is a synthetic form of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), also known as luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH). It is a decapeptide (10 amino acids) that is identical to the naturally occurring GnRH produced by the hypothalamus. GnRH is the master regulator of the reproductive system, controlling the release of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the pituitary gland.
As a pharmaceutical product, gonadorelin has been used diagnostically to assess pituitary function and therapeutically in specific reproductive disorders. Its pulsatile administration can stimulate gonadotropin secretion, while continuous administration leads to receptor downregulation and suppression of the reproductive axis.
Mechanism of Action
Gonadorelin binds to GnRH receptors on gonadotroph cells in the anterior pituitary gland. This activates G-protein coupled receptor signaling pathways, leading to increased synthesis and secretion of luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). The released gonadotropins then act on the gonads (testes and ovaries) to stimulate sex hormone production and gametogenesis.
The response to gonadorelin is highly dependent on the pattern of administration. Pulsatile delivery (mimicking natural GnRH secretion) maintains and stimulates gonadotropin release. Continuous exposure leads to GnRH receptor downregulation and desensitization, paradoxically suppressing LH and FSH secretion - a property exploited therapeutically by long-acting GnRH agonists.
Research Findings
Research on gonadorelin and the GnRH system has been fundamental to understanding reproductive endocrinology. Diagnostic studies have used gonadorelin stimulation tests to assess pituitary gonadotroph function and differentiate between hypothalamic and pituitary causes of hypogonadism. Clinical research has shown that pulsatile gonadorelin administration can induce ovulation in women with hypothalamic amenorrhea and stimulate spermatogenesis in men with hypogonadotropic hypogonadism.
Reproductive Medicine Applications
Studies in assisted reproductive technology have explored gonadorelin for ovulation induction, though it has largely been supplanted by recombinant gonadotropins for practical reasons. Research into the pulsatile GnRH system has elucidated critical aspects of reproductive physiology, including the importance of pulse frequency in determining LH versus FSH dominance.
Research Applications
- Pituitary function testing and diagnostics
- Hypogonadotropic hypogonadism research
- Ovulation induction studies
- GnRH receptor pharmacology research
- Reproductive axis regulation studies
- Pulse generator and hypothalamic function research
Safety Profile
Gonadorelin is generally well-tolerated when used appropriately. Side effects are typically mild and may include headache, nausea, abdominal discomfort, and local injection site reactions with subcutaneous administration. Allergic reactions are rare. The primary safety consideration is appropriate patient selection and monitoring of reproductive hormone responses. Gonadorelin is approved for diagnostic use in many countries. Therapeutic use requires pulsatile delivery systems which are complex and expensive, limiting practical application.
Scientific References
Research Use Only
This product is intended for research purposes only and is not for human consumption, therapeutic use, or diagnostic applications. Please ensure compliance with all applicable regulations and institutional guidelines.